
Automatic multi-row sheet metal storage system is a high-density storage and intelligent management solution for sheet metal processing companies. It is suitable for production environments that require centralized storage and automated retrieval of a variety of sheet metal specifications.
It combines a multi-layered shelving system with an automated handling and management system to significantly improve storage and retrieval efficiency, reduce floor space, and mitigate the risks of manual handling.
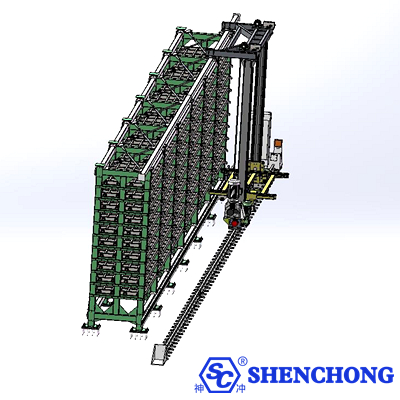
The structure of the multi-row sheet metal storage system can be understood as consisting of four major components: multi-row three-dimensional shelving + automated handling system + information control system + safety protection. Each component is further divided into several key modules:
Arranged in multiple rows (inline, back-to-back, or circular layouts).
With a multi-layer structure, each compartment can store a full package of sheet metal (common sizes include 3 x 1.5m and 4 x 2m).
High-strength steel construction with a rust-resistant surface treatment.
Specialized steel pallets facilitate handling.
Supports mixed storage of sheets of varying thicknesses and materials.
Transport aisles or rails are reserved between rows.
Operate in front of or in the middle aisles of multiple rows of shelves.
Equipped with a lifting platform, telescopic arm, or vacuum suction cup gripping device.
Enables vertical loading and unloading of multiple shelves.
Usually utilizes a chain or screw lift mechanism.
Reaches into the shelves to retrieve pallets or sheets.
Vacuum suction cups are suitable for preventing scratches on the sheets.
Connects to the loading and unloading platforms of equipment such as laser cutters and press brakes.
This can be a roller conveyor, chain conveyor, or belt conveyor.
Controls transport trolleys, lifting, conveying, and other operations; Manages the coordinated operation of multiple rows of shelves
Automatically records sheet material inbound, outbound, and inventory information
Interface with ERP/MES systems to enable on-demand material adjustments
Automatically calculates the shortest material retrieval route, reducing handling wait times
Operators can quickly retrieve or put materials into storage via the touchscreen
Photoelectric Sensors: Detect the presence of sheet materials in the cargo area to prevent misoperation
Weight Detection: Prevents overloading
Anti-Collision System: Automatically avoids obstacles during operation
Emergency Stop and Safety Door: Ensure safety during maintenance
Fire Protection and Security: Some systems are equipped with smoke and temperature monitoring
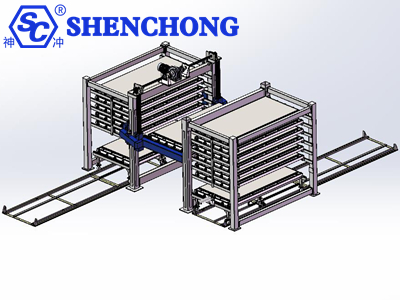
The core operating principle of a multi-row automated sheet metal warehouse is based on on-demand material selection, automated handling, and intelligent path planning. Through the coordination of multiple rows of three-dimensional racks and handling mechanisms, the entire process of sheet metal inbound, storage, and outbound is automated.
This process is divided into four stages: inbound → storage management → outbound → multi-row coordination.
A forklift, automatic loading platform, or conveyor delivers the entire package of plates to the inbound workstation.
The system scans or manually enters plate material, thickness, specification, batch, and other information.
A transport cart/crane moves to the inbound location, where a suction cup or fork arm grabs the plate pallet.
A lifting device delivers the plates to the target level, and a telescopic arm pushes them into the designated bay.
The WMS system automatically allocates storage locations based on plate type, thickness, and production schedule.
Frequently used plates are placed near the outbound end or in lower bays to reduce retrieval time.
Occupancy status, remaining quantity, and plate information for each bay are updated in real time.
The MES/ERP system transmits information about the plates required for production to the warehouse management system.
Automatically plans material retrieval routes (avoids detours and reduces waiting).
The handling cart/trolley moves to the target shelf → raises and lowers to the corresponding level → the telescopic arm/suction cup grabs the plate pallet.
The plates are delivered to the upper and lower loading stations of equipment such as laser cutters and press brakes, ensuring seamless connection.
The handling mechanism can service multiple rows of shelves, switching between left and right, or forward and backward, to retrieve materials.
The system optimizes the order of material retrieval based on factors such as task priority, distance, and sheet weight.
Supports simultaneous loading and unloading without interfering with each other.
Information flow drives material flow: Inventory information + production plan → automatically generate handling tasks.
Optimal path planning: Reduces cart travel time and improves outbound efficiency.
Multi-row rack coordination: A single handling system efficiently serves multiple rows of warehouses.
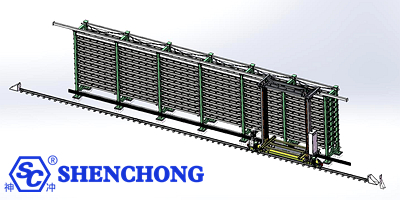
The core advantages of the multi-row sheet metal storage system can be summarized as "high-density storage + high-efficiency scheduling + highly flexible layout + high-security management." It is suitable for sheet metal factories with a wide variety of sheet metal products, frequent material usage, and multiple production lines.
Within the same floor space, storage capacity is 3-6 times higher than traditional flat warehouses.
Supports mixed storage of sheet metal of varying sizes, thicknesses, and materials.
Shelf levels can be designed based on factory height, maximizing vertical space utilization.
Optimizes material handling paths, reducing idle handling and waiting time.
Stocking and outgoing materials can be processed simultaneously without interfering with each other.
Directly connects to laser cutting machines, press brakes, and other equipment to achieve continuous production.
Linear, back-to-back, U-shaped, and circular layouts are available to accommodate various factory structures.
Shelf rows or layers can be added later for easy expansion.
One handling system can supply multiple production lines.
Reduced heavy object handling and sheet material scratching accidents.
Photoelectric detection, anti-collision protection, and weight monitoring ensure equipment and personnel safety.
Incoming and outgoing records for each batch of sheet materials are traceable, preventing material errors and leaks.
Centralized sheet material management reduces floor clutter.
Precise inventory management avoids over-purchasing and backlogs.
Integrated with ERP/MES systems, laying the foundation for smart factories.
Typical applications for multi-row automated sheet metal storage systems are primarily concentrated in sheet metal processing and manufacturing industries, where a wide variety of sheet materials are processed frequently and multiple production lines are required. Its features include centralized, high-density storage, automated, rapid retrieval, and direct connection to production lines, resulting in a wide range of applications.
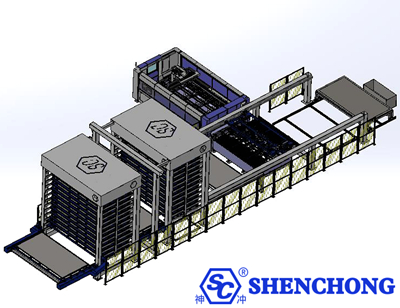
Features: Accepts large volumes of outsourced orders, with a wide variety of sheet material specifications and frequent material changes.
Application Value:
Consolidated management of sheet materials for different customers reduces material errors.
Quickly switches between sheets required for orders, improving capacity utilization.
Features: Large numbers of laser cutting machines, high output, and high loading speed requirements.
Application Value:
Multi-row storage systems can simultaneously feed multiple laser machines.
Shortening sheet material changeover time and enabling continuous processing.
Features: Requires sheet materials of various thicknesses and materials (cold-rolled steel, stainless steel, galvanized steel, etc.).
Application Value:
Classified storage of different materials to prevent material mixing.
Forms an automated loading and unloading closed loop with press brakes and punching machines.
Features: High-variety, small-batch production with frequent switching between production tasks.
Application Value:
Reduces manual handling and material retrieval time.
Improve production flexibility and adapt to rapid changeovers.
Features: Large and heavy sheet metals pose a high risk of manual handling.
Application Value:
High-strength three-dimensional racking safely stores heavy sheet metal.
Automated handling reduces labor costs and the risk of work-related injuries.
Features: Strives for full-process automation and information management.
Application Value:
Interfaces with MES/ERP to form an intelligent warehousing-processing-distribution closed loop.
Achieve real-time inventory visualization and linkage with production planning.
The core structure of the automatic multi-row sheet metal storage system is the storage density provided by the multi-row three-dimensional racking, the precise loading and unloading system, the control system that enables efficient and coordinated operation of the multiple rows, and the safety system that ensures stable operation.